Bone pain – especially hip and low back pain muscle weakness fatigue pathological # hypocalcaemia – perioral and extremity numbness hand/foot spasms arrhythmias. Bone pain skeletal deformity e.g bow legs, pigeon chest pathological # poor growth muscle weakness dental deformities. Leads to low calcium and phosphate, and secondary hyperparathyroidism. Inadequate mineralisation of bone matrix.
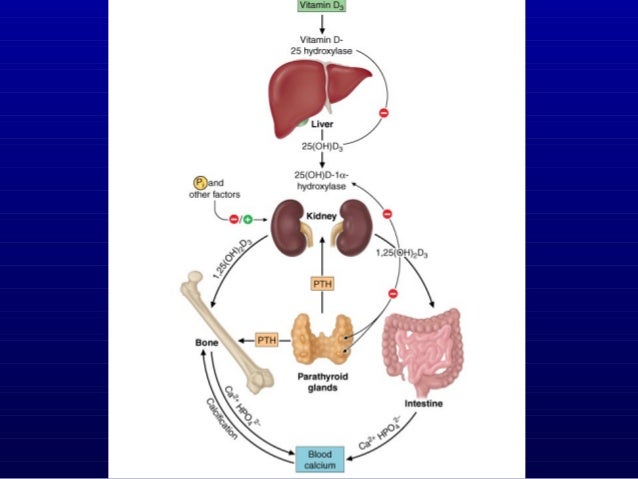
Skin and dietary sources of vitamin D are metabolised by liver and then kidney, into active form 1,25hydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol). Eggs, dairy products, oily fish, fortified cereals. Diet adequate in vitamin D is needed to maintain supplies in Winter (D2 and D3). Vitamin D is produced by the skin in sunlight (cholecalciferol - D3). Absorption of calcium from blood into bone matrix, stimulated by calcitriol. PTH causes release of calcium from bone into bloodstream. Dairy (semi skimmed milk greater content than full fat), sardines, bread, baked beans, cabbage. Calcitriol acts to aid absorption of calcium from small intestine. It also increases kidney’s reabsorption of calcium from urine In kidney, PTH turns vitamin D into its active form 1,25hydroxycholecalciferol (calcitriol).